Service
A service is defined by ISO 20000, the international standard for service management, as 'a means of delivering value for the customer by facilitating outcomes the customer wants to achieve' [1].
Typical examples of services are information technology services such as applications hosted in the cloud, education and training services or medical services.
Common types of services are:
- Customer-facing services, provided to customers outside the organization
- internal services, provided by one unit to one or several other units in the same organization
- external supporting services, provided to the organization by third-party suppliers.
Services vs. products
Products and services are related concepts, and looking at the differences between them helps to better understand the nature of services:
- Products are tangible or intangible items that are usually owned by the consumer and that can be moved, returned or replaced. Products can be produced in advance.
- Services are work or benefits provided to customers on demand. Services cannot be produced in advance.
Successful businesses often combine products and services to offer a complete "solution" to their customers. For example, a manufacturer of elevators may sell its products and in addition provide services, such as on-site assembly, regular maintenance and emergency assistance.
Services thus enhance the value of products to customers and allow businesses to maintain a long-term relationship with their clients.
Customer-facing services
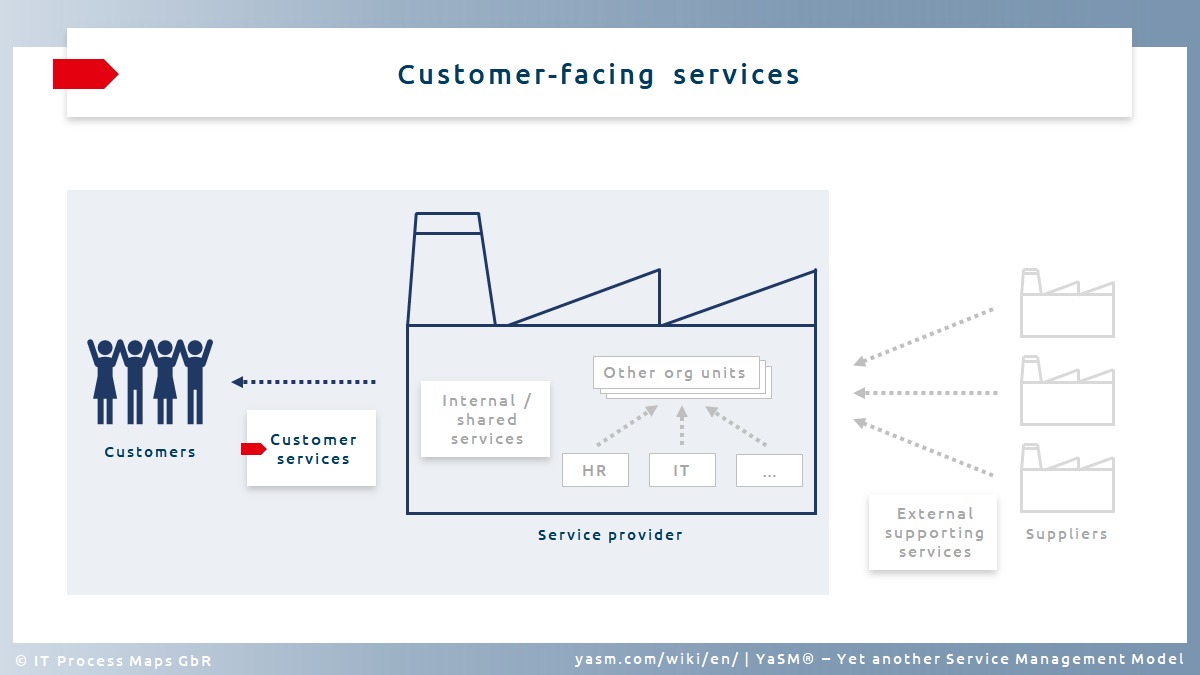
Customer‑facing services are provided to consumers outside the organization.
Typical examples are
- transportation services
- healthcare services
- financial services
- etc.
Many organizations apply the methods of service management not only to their customer-facing services, but also to internal services.
Internal services are delivered by one unit to one or several other units in the same organization. Examples of internal services are
- HR services
- IT services
- facility services
- procurement services
- etc.
Internal services are often provided as part of a shared services model that allows businesses to cluster similar resources and increase their operating efficiency. Shared services typically deliver technical and administrative support in areas common to all business units in a company. In many cases, they underpin core business functions.
Service integrators using external supporting services
Service providers typically outsource some of the work to external suppliers. Service providers thus act as "service integrators", which allows them to adopt a more flexible model, using external supporting services as needed.
Service integrators aggregate and consolidate the services provided by multiple suppliers to deliver a cohesive and reliable portfolio of services to the customers.
For service integration to work, organizations need to manage the relationship, contracts and performance of external suppliers, which calls for a robust supplier management process.
Related topics
Notes and references
[1] ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018. Information technology - Service management - Part 1: Service management system requirements. International Organization for Standardization ISO, 2018. Retrieved February 12, 2021.
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() and Andrea Kempter
and Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
What is a service? › Services vs. products › Customer-facing services › Internal services and shared services › External supporting services






