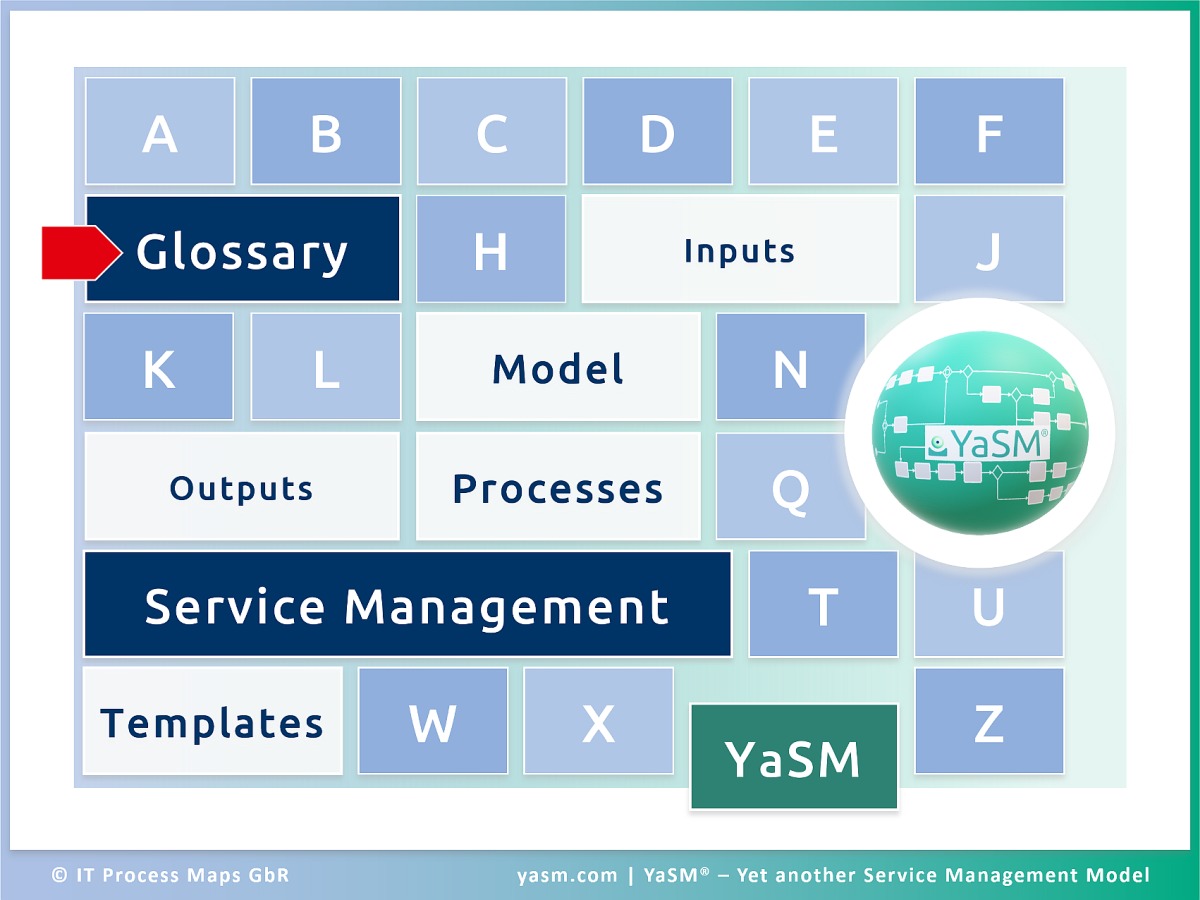
YaSM Glossary
All terms and definitions related to service management:
The YaSM® service management glossary contains definitions or short descriptions of the YaSM data objects or key terms in enterprise service management, business service management, ITSM, and ISO 20000 in alphabetical order.
- Related contents of this YaSM wiki, like YaSM process definitions and role descriptions can be reached via links.
- On another page you can find the complete YaSM data object model - a graphical overview of the YaSM data objects and their key interrelationships.
In addition to the glossary, the YaSM® Process Map contains a set of "service management checklists":
These are document templates with very detailed descriptions of the typical contents of the various YaSM documents and records (as a rule, every YaSM data object corresponds to a document or record produced in a service management process). Because the checklists are Microsoft Word documents, they can often be used as templates when creating the service management documents for a particular organization.
This wiki contains - among other document templates - the full checklist for the incident record as an example.
| YaSM service management glossary terms |
Browse alphabetically:
| 0 ... 9 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | ||||||||||||
| N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
Other languages: The YaSM glossary, German version.
Note: Some definitions in this glossary are based on the official ITIL® [2] Glossary [3].
All YaSM Terms
0-9
- 1st level support
- (→ YaSM role, 1st level support)
- 2nd level support
- (→ YaSM role, 2nd level support)
A
- Application/ System developer
- (→ YaSM role, Application/ System developer)
- Assess and coordinate changes
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
B
- Budget request
- A budget request is typically issued to obtain funding for setting up, improving or operating a service or process. An approved budget request means that the required financial resources have been allocated by the financial manager.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
- Build new or changed services
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP3: Build new or changed services)
C
- CAB meeting minutes
- The CAB meeting minutes document the topics discussed in a change advisory board (CAB) meeting and any decisions taken. A draft of this document can be circulated in preparation of the CAB meeting to inform the CAB members of agenda items to be dealt with.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change advisory board (CAB)
- (→ YaSM role, Change advisory board (CAB))
- Change assessment report
- The results of a change assessment are documented in a change assessment report. Every non-standard change requires formal assessment before being authorized. Particular changes may require more extensive assessments than others, so the contents of the assessment report will depend on the nature and scope of the proposed change.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change enablement
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change manager
- (→ YaSM role, Change manager)
- Change model
- Change models describe procedures for the handling of recurring changes. While change models can be created for changes of any scale, they are often used to define standard changes (low-risk, pre-authorized changes like installing additional hardware on a client PC). Change models are an important tool to reduce the workload of the change manager and the CAB.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change owner
- (→ YaSM role, Change owner)
- Change policy
- The change policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to dealing with changes to configuration items (CIs). To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change record
- A change record contains all details of a change, documenting the lifecycle of a single change. In its initial state, a change record describes a request for change (RFC) which is to be assessed and authorized prior to implementing the change. Further information is added as the change progresses through its lifecycle.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Change schedule
- The change schedule lists all proposed and authorized changes, including their planned and actual implementation dates. It is sometimes called a forward schedule of change, even though it also contains information about changes that have already been implemented.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- CI record
- Configuration information is maintained in CI records for all configuration items (CIs) under the control of the configuration manager. In this context, CIs can be of various types: Applications, systems and other infrastructure components are treated as CIs, but often also services, policies, project documentation, employees, suppliers, etc. Configuration information is stored in the configuration management system (CMS).
(→ YaSM data object, SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Complaint record
- A record containing the details of a customer complaint, including the actions taken to resolve the complaint.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Compliance management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP9: Ensure compliance)
- Compliance manager
- (→ YaSM role, Compliance manager)
- Compliance policy
- The compliance policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to ensuring compliance with legal requirements, industry standards, etc. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP9: Ensure compliance)
- Compliance register
- The compliance register is a tool used by the compliance manager to keep an overview of all compliance requirements applicable to the service provider. The compliance register also states the controls and mechanisms put in place to ensure the service provider organization fulfills the compliance requirements.
(→ YaSM data object, SP9: Ensure compliance)
- Compliance review report
- A compliance review report records the details and findings from a compliance review or audit. This report is an important input for improving the service provider's compliance with legal requirements, industry standards, etc.
(→ YaSM data object, SP9: Ensure compliance)
- Configuration audit report
- A report summarizing the results of a configuration audit, highlighting revealed differences between the CI records in the CMS and actually installed CIs.
(→ YaSM data object, SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Configuration management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Configuration manager
- (→ YaSM role, Configuration manager)
- Configuration model
- The configuration model defines the structure of the configuration management system (CMS). It specifies the types of configuration items (CIs) to be managed through the CMS, including their attributes. The configuration model is often maintained as a set of documents or a data model. It also manifests itself, for example, in the table structure of the database(s) used to store configuration information.
(→ YaSM data object, SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Configuration policy
- The configuration policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing configuration information. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Continual improvement
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP5: Improve the services)
- Continuity improvement plan
- Items in the continuity improvement plan are used by the service continuity manager to record and manage continuity improvement initiatives throughout their lifecycle. Initiatives in the continuity improvement plan may aim to enhance the resilience of services or to put mechanisms in place for the recovery of services in the case of critical events.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Continuity operation manual
- The continuity operation manual specifies the activities required for the operation of the continuity arrangements and mechanisms operated under the responsibility of the service continuity manager. Some instructions related to the operation of particular security systems may be documented in separate technical manuals or "standard operating procedures (SOPs)".
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Continuity policy
- The continuity policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to preparing itself for critical, disruptive events, with the aim of ensuring service continuity. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Continuity review report
- A continuity review report records the details and findings from a continuity review. This report is an important input for the definition of continuity improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Customer meeting minutes
- The customer meeting minutes record the details and findings from a meeting of the service provider with one of its customers. This report is an important input for developing the service strategy and defining service improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer portfolio
- The customer portfolio is used to record all information related to customers. The customer portfolio is the customer relationship manager's view of the customers who receive services from the service provider.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer process
- Customer process denotes all business processes on the client or user side.
(→ YaSM process, external process)
- Customer relationship management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer relationship manager
- (→ YaSM role, Customer relationship manager)
- Customer relationship policy
- The customer relationship policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing customer relationships. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer service agreement
- An agreement between a service provider and a customer for the provision of a service as specified in the service definition. A signed customer service agreement represents a commitment by the service provider to deliver a service in line with the agreed quality, at a specified cost. A single agreement may cover multiple services.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer survey evaluation
- The evaluation of a customer satisfaction survey, presenting the results and findings from the survey in a condensed way.
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer survey questionnaire
- A customer survey is typically based on questionnaires, aimed at getting insight into overall customer satisfaction and customers' views on specific (aspects of) services. In many cases, answers are given using a scale, for example "1: Very dissatisfied", ... , "10: Very satisfied".
(→ YaSM data object, SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Customer
- (→ YaSM role, Customer)
→ YaSM terms starting with "C"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
D
- Design new or changed services
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP2: Design new or changed services)
E
- Emergency change advisory board (ECAB)
- (→ YaSM role, Emergency change advisory board (ECAB))
- Ensure compliance
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP9: Ensure compliance)
- Ensure continuity
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Ensure security
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP7: Ensure security)
- External service agreement
- An agreement between a service provider and an external supplier for supplying a supporting service as specified in the service definition. A signed external service agreement represents a commitment by an external service supplier to supply a supporting service in line with the agreed quality, at a specified cost. A single agreement may cover multiple services.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- External supplier process
- External supplier process denotes all processes on the side of external suppliers.
(→ YaSM process, external process)
→ YaSM terms starting with "E"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
F
- Financial budget
- The financial budget is a financial plan, typically prepared on an annual basis, which provides a forecast of expected revenues and expenditures.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
- Financial management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP12: Manage service financials)
- Financial manager
- (→ YaSM role, Financial manager)
- Financial policy
- The financial policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing service financials, including invoicing customers for service provision. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
- Financial report
- Financial reports are an important input for developing the service provider's strategy and devising initiatives to improve service economics. In particular, financial reports contain information on the costs of providing services and operating the service management processes. They also provide insight into the profitability of the different service offerings.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
→ YaSM terms starting with "F"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
G
- Guideline for critical events
- The guideline for critical events contains detailed instructions on when and how to invoke the procedure for responding to critical, disruptive events. Most importantly, the guideline defines the first steps to be taken by 1st level support after learning that a (suspected) critical event has occurred.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
H
- Human Resource Management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP10: Manage human resources)
- Human resources manager
- (→ YaSM role, Human resources manager)
- Human resources policy
- The human resources (HR) policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing human resources, including the skills required to deliver the service provider's range of services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP10: Manage human resources)
I
- Improve the services
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP5: Improve the services)
- Incident and service request policy
- The incident and service request policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to dealing with service incidents (service failures) and service requests. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Incident management
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Incident manager
- (→ YaSM role, Incident manager)
- Incident model
- An incident model contains the pre-defined steps that should be taken for dealing with a particular type of incident. The aim of providing incident models is to ensure that recurring incidents are handled efficiently and effectively.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Incident record
- A set of data with all details of a service incident, documenting the history of the incident from registration to closure. A service incident is defined as an unplanned interruption or reduction in quality of a service. Events that could potentially impair a service in the future are also treated as incidents (e.g. the failure of one hard-drive of a set of mirrored drives). (See also: → YaSM incident record template).
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Incident record)
- Index of continuity-relevant information
- A catalogue of all information that is relevant in the context of responding to critical, disruptive events. This index is maintained and circulated by the service continuity manager to all members of staff with responsibilities for fighting critical events.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Indirect cost allocation table
- Indirect cost allocation tables are a method for dividing up costs which are shared across multiple cost centers (for example services). An indirect cost allocation table defines the rules for allocating such indirect costs to particular cost centers.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
- Information security management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP7: Ensure security)
- IT asset management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP4: Manage configuration information)
→ YaSM terms starting with "I"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
M
- Maintain the service portfolio
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Major incident team
- (→ YaSM role, Major incident team)
- Manage configuration information
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Manage customer relationships
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Manage human resources
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP10: Manage human resources)
- Manage projects
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP6: Manage projects)
- Manage service financials
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP12: Manage service financials)
- Manage suppliers
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Monitoring and event management
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services)
→ YaSM terms starting with "M"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
O
- Operate the services
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services)
- Operational service agreement
- An agreement between a service provider and a part of the same organization for supplying a supporting service as specified in the service definition. A signed operational service agreement represents a commitment by an organizational unit within the service provider to supply a supporting service in line with the agreed quality, at a specified cost. A single agreement may cover multiple services.
(→ YaSM data object, SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Operations manager
- (→ YaSM role, Operations manager)
- Operator
- (→ YaSM role, Operator)
→ YaSM terms starting with "O"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
P
- Planned service outages
- The planned service outages document or database lists any expected or planned deviations from normal service availability, such as outages due to maintenance work or the implementation of changes.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services)
- Portfolio management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Post-implementation review report
- The results of a post-implementation review are documented in a post-implementation review report. Post-implementation reviews (PIR) take place after a change has been implemented. Their aim is to determine if the change was successful and to identify improvement opportunities for future changes.
(→ YaSM data object, SP5: Assess and coordinate changes)
- Problem management
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services > LP4.7: Resolve problems)
- Problem manager
- (→ YaSM role, Problem manager)
- Problem record
- A set of data with all details of a problem, documenting the history of the problem from registration to closure. A problem is defined as the underlying cause of one or more (potential) incidents, although the cause may not be known at the time a problem record is created. Often, a workaround is provided for a problem while a full resolution is not yet available.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.7: Resolve problems)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Problem record)
- Problem resolution policy
- The problem resolution policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to dealing with problems (underlying causes of incidents). To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.7: Resolve problems)
- Process improvement plan - PIP
- Items in the process improvement plan (PIP) are used to record and manage process improvement initiatives throughout their lifecycle. There may be one process improvement plan for all processes or dedicated plans for particular processes managed by the service provider. The addition of new items to the PIP is often triggered by process reviews, although suggestions to improve processes may also come from other sources.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Process metric
- Process metrics are used to help manage a process. They are often designed to measure if a process is running successfully. As such, they are an essential input for continual process improvement. Process metrics also play an important role in steering the service provider's resources.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Process model
- The process model provides an overview of the service management processes. It typically contains high-level views to illustrate the structure and interdependencies of the processes, and more detailed views to describe the processes' inputs and outputs, activities and responsibilities. The process model is an important tool for ensuring that all processes within the service provider organization cooperate in a seamless way.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Process operation manual
- A process operation manual specifies the activities required for the operation of a process and its underlying infrastructure. The information in the process operation manual is meant to describe the day-to-day tasks in a way that is useful for operational staff. Some instructions related to the operation of particular applications, systems or other infrastructure components may be documented in separate technical manuals or "standard operating procedures (SOPs)".
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Process owner
- (→ YaSM role, Process owner)
- Process review plan
- The process review plan is maintained by the SMS manager to ensure all relevant processes and areas of the service provider organization are subjected to regular management reviews, audits, benchmarkings or maturity assessments, as appropriate.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Process review report
- A process review report records the details and findings from a process review or audit. This report is an important input for the definition of process improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Process review report)
- Project board
- (→ YaSM role, Project board)
- Project charter
- A project charter is a document that formally authorizes a project. It outlines the project objectives and scope, identifies the main stakeholders, defines the authority of the project manager and the resources at his disposal, and lists any constraints and assumptions affecting the project.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
- Project issue log
- The project issue log is a document recording important issues and events during the course of a project, in particular issues which require action by the project board or higher levels of management. The issue log is an important tool for managing open issues, but it is also a means of documenting significant events such as decisions to update the project scope or the project milestones.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
- Project management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP6: Manage projects)
- Project manager
- (→ YaSM role, Project manager)
- Project owner
- (→ YaSM role, Project owner)
- Project plan
- A project plan is a formal, approved document showing the deliverables, milestones, activities and resources for a project. Project plans are used to guide both project execution and project control.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
- Project policy
- The project policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing projects. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
- Project review report
- The results of a project review are documented in a project review report. Project reviews take place during formal project closure. Their aim is to determine if the project was successful and to identify opportunities for improvement.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
- Project status report
- A project status report is generated at regular intervals during the course of a project. It provides an overview of the current project status and highlights, in particular, any deviations regarding project scope, schedule and cost, including measures taken to address the deviations.
(→ YaSM data object, SP6: Manage projects)
→ YaSM terms starting with "P"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
R
- Recovery plan
- Recovery plans contain detailed instructions for returning specific services and/ or systems to a working state, which often includes recovering data to a defined consistent state.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services)
- Register of managed critical events
- The register of managed critical events is a tool used by the service continuity manager to keep an overview of the critical events against which the service provider has decided to set up some kind of protection, considering the potential impacts and occurrence likelihoods. The register of managed critical events also specifies the responses to the identified events, in particular the related service continuity plans.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Register of security risks
- The register of security risks is a tool used by the security manager to keep an overview of all security risks to be managed. The register of security risks also specifies the responses to the identified risks, in particular security controls and mechanisms to mitigate the risks.
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
- Relationship management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP3: Manage customer relationships)
- Release management
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP3: Build new or changed services)
- Requirements specification
- A requirements specification document contains a complete description of the behavior of an application, system or other infrastructure item that is to be developed or acquired. Requirements specifications typically include functional and non-functional requirements, such as performance requirements or design constraints. The contents and degree of detail will vary depending on the nature of the system specified and the purpose of the specification.
(→ YaSM data object, LP2: Design new or changed services)
- Resolve incidents and service requests
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Resolve problems
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services > LP4.7: Resolve problems)
- Risk management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP7: Ensure security)
→ YaSM terms starting with "R"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
S
- Security improvement plan
- Items in the security improvement plan are used by the security manager to record and manage security improvement initiatives throughout their lifecycle. Initiatives in the security improvement plan may aim to implement proactive measures to enhance security or to put mechanisms in place which allow responding effectively to any security breaches.
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
- Security management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP7: Ensure security)
- Security manager
- (→ YaSM role, Security manager)
- Security operation manual
- The security operation manual specifies the activities required for the operation of the security controls and mechanisms operated under the responsibility of the security manager. Some instructions related to the operation of particular security systems may be documented in separate technical manuals or "standard operating procedures (SOPs)".
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
- Security policy
- The security policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to ensuring security. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
- Security review report
- A security review report records the details and findings from a security review. This report is an important input for the definition of security improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
- Service
- A means of delivering value to customers by facilitating outcomes customers want to achieve without the ownership of specific costs and risks. YaSM defines the properties of a service in a service definition. (→ See Service definition).
- Service build policy
- The service build policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to implementing new or significantly changed services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP3: Build new or changed services)
- Service catalog
- A service catalog is a special view of the information in the service portfolio for current or prospective customers. Service catalogs are often "interactive", allowing customers and users, for example, to raise incidents or service requests. There may be several service catalogs, for instance for specific (groups of) customers or purposes. (→ See Service portfolio)
- Service catalogue management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Service configuration management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP4: Manage configuration information)
- Service continuity management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Service continuity manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service continuity manager)
- Service continuity plan
- A service continuity plan describes how service continuity is ensured with regards to a particular type of critical event. The plan specifies the required preventive measures and describes how to effectively respond to the critical event. Service continuity plans usually include references to more detailed recovery plans with specific instructions for returning applications, systems or other infrastructure components to a working state.
(→ YaSM data object, SP8: Ensure continuity)
- Service definition
- A service definition specifies the service properties, in particular the offered functionality and the guaranteed service levels. Service definitions also describe how the organization's resources are used in order to provide the service. A service can be provided using one or several other (internal or external) supporting services.
(→ YaSM data object, SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Service definition)
- Service design
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP2: Design new or changed services)
- Service design manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service design manager)
- Service design policy
- The service design policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to designing new or significantly changed services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, service lifecycle processes > LP2: Design new or changed services)
- Service financial management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP12: Manage service financials)
- Service implementation manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service implementation manager)
- Service implementation blueprint
- The service implementation blueprint builds upon the specifications in the service definitions. It describes from a technical and organizational perspective what capabilities are required in order to be able to offer a new or changed service, and outlines the approach to creating the required service infrastructure and other capabilities. The service implementation blueprint is an important input for project planning and service implementation.
(→ YaSM data object, LP2: Design new or changed services)
- Service improvement manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service improvement manager)
- Service improvement plan - SIP
- The service improvement plan (SIP) is used to manage service improvement initiatives and report on their status throughout their lifecycle. There may be one service improvement plan for all services or dedicated plans for the various services managed by the service provider. The addition of new items to the SIP is often triggered by service reviews, although other service management processes may also suggest improvements to services.
(→ YaSM data object, LP5: Improve the services)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Service improvement plan - SIP)
- Service improvement policy
- The service improvement policy describes and communicates the service provider's approach to continually improving its services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP5: Improve the services)
- Service lifecycle processes
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes in YaSM service management)
- Service management policies
- The service management policies represent a key element of the service management system, defining principles and rules to be followed in the service provider organization. The set of service management policies includes a top-level service management policy which is supported by a number of specific policies for the various service management processes.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Service management policy
- The service management policy describes and communicates the service provider's approach to managing and delivering its services through a service management system (SMS). The service management policy represents the top level in the hierarchy of policies; it is supported by a number of specific policies for the various service management processes. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Service management system - SMS
- A management system to direct and control the service management activities of the service provider. Key components of the SMS are the service management policies and the service management processes, including the resources required to support the service management processes.
- Service operation
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP4: Operate the services)
- Service operation manual
- A service operation manual specifies the activities required for the operation of a service and its underlying infrastructure. The information in the service operation manual is meant to describe the day-to-day tasks in a way that is useful for operational staff. Some instructions related to the operation of particular applications, systems or other infrastructure components may be documented in separate technical manuals or "standard operating procedures (SOPs)".
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services)
- Service operation policy
- The service operation policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to operating its range of services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services)
- Service owner
- (→ YaSM role, Service owner)
- Service portfolio manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service portfolio manager)
- Service portfolio policy
- The service portfolio policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to maintaining the service provider's range of services (the "service portfolio"). To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Service portfolio review report
- A service portfolio review report records the details and findings from a service portfolio review. In particular, this report will highlight any detected inconsistencies within the service portfolio.
(→ YaSM data object, SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
- Service portfolio
- The service portfolio represents a complete list of all services managed by the service provider. Some of these services are visible to the customers (customer services), while others are not (supporting services, which can be provided with internal or external resources).
(→ YaSM data object, SP2: Maintain the service portfolio)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Service portfolio)
- Service quality report
- A service quality report gives insight into the service provider's ability to deliver the agreed service quality. Most importantly, it reports on the service levels achieved in relation to the agreed targets, as specified in the service definitions. Service quality reports will also highlight any breaches of contractual commitments and exceptional events.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services)
(→ YaSM checklist / document template: Service quality report)
- Service readiness confirmation
- The service readiness confirmation documents the results of a service readiness assessment. A service is assessed for readiness before being allowed to go operational, using a set of criteria that relate, in particular, to the service provider's ability to operate the service. Once it is confirmed that the service readiness criteria are fulfilled, a service can be marked as "active" in the service portfolio.
(→ YaSM data object, LP3: Build new or changed services)
- Service request fulfillment group
- (→ YaSM role, Service request fulfillment group)
- Service request model
- Service request models contain the pre-defined steps that should be taken for dealing with a particular type of service request. The aim of providing service request models is to ensure that routinely occurring requests are handled efficiently and effectively.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Service request record
- A record containing all details of a service request. Service requests are formal requests from a client or user for something to be provided within the framework of existing service agreements - for example, a request for information or advice; to reset a password; or to install a workstation for a new user.
(→ YaSM data object, LP4: Operate the services > LP4.6: Resolve incidents and service requests)
- Service review report
- A service review report records the details and findings from a service review. This report is an important input for the definition of service improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, LP5: Improve the services)
- Service strategy manager
- (→ YaSM role, Service strategy manager)
- Service strategy policy
- The service strategy policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing the service provider's strategy and range of services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Service validation and testing
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP3: Build new or changed services)
- Set the strategic direction
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Set up and maintain the service management system
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- Skills development plan
- The skills development plan is used to manage the acquisition of the skills required to deliver the service provider's range of services. The addition of new items to the skills development plan is often triggered by the introduction of new services and/ or technologies.
(→ YaSM data object, SP10: Manage human resources)
- Skills inventory
- The skills inventory identifies the skills required to deliver the service provider's current and future range of services, as well as the individuals who possess those skills. The skills inventory is an important tool for identifying areas where skills need to be developed or improved.
(→ YaSM data object, SP10: Manage human resources)
- SMS maintenance
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP1: Set up and maintain the service management system)
- SMS manager
- (→ YaSM role, SMS manager)
- Specification of financial data categories
- The specification of financial data categories lists and defines the various categories used to structure financial data in order to gain insight into the costs of service provisioning and service profitability.
(→ YaSM data object, SP12: Manage service financials)
- Steering group
- (→ YaSM role, Steering group)
- Strategic assessment report
- The results of a strategic assessment are documented in a strategic assessment report. Strategic assessments typically take place at regular intervals in order to gain insight into the service provider's strengths, weaknesses and opportunities prior to updating the service strategy and the portfolio of services.
(→ YaSM data object, LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Strategic objectives
- The strategic objectives are formulated once a strategic assessment has been completed. They consist of a set of specific goals the service provider aims to achieve by pursuing the service strategy. As such, the strategic objectives are an important input for defining the strategic plan.
(→ YaSM data object, LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Strategic plan
- The strategic plan (at times referred to as the "service strategy") identifies how the service provider will achieve its strategic objectives. It is used to manage strategic initiatives and report on their status throughout their lifecycle. The addition of new items to the strategic plan is often triggered by strategic assessments, although other service management processes may also suggest strategic initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Strategy management
- (→ YaSM process, service lifecycle processes > LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Supplier dispute record
- A record containing the details of a supplier dispute, including the actions taken to resolve the issue.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supplier management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supplier manager
- (→ YaSM role, Supplier manager)
- Supplier meeting minutes
- The supplier meeting minutes record the details and findings from a meeting of the service provider with one of its external service suppliers. This report is an important input for defining service improvement initiatives.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supplier policy
- The supplier policy describes and communicates the organization's approach to managing external suppliers of goods and services. To be effective, the policy needs the backing of top management and must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supplier portfolio
- The supplier portfolio is used to record all information related to suppliers. The supplier portfolio is the supplier manager's view of the external suppliers which provide goods and services to the service provider.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supplier review report
- A supplier review report provides insight into a supplier's ability to fulfill their contractual obligations. In particular, it reports on the service levels achieved in relation to the agreed targets, as specified in the service definitions. Supplier review reports will also highlight any breaches of contractual commitments and exceptional events.
(→ YaSM data object, SP11: Manage suppliers)
- Supporting processes
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes in YaSM service management)
- System developer
- (→ YaSM role, Application/ System developer)
→ YaSM terms starting with "S"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
T
- Technical domain expert
- (→ YaSM role, Technical domain expert)
- Technology guideline
- The technology guideline provides a high-level overview of the main infrastructure components and technologies as well as a roadmap for their future development. The technology guideline's main purposes are to align the service provider's technical infrastructure with its strategic objectives, and to help the organization focus on a set of core technologies.
(→ YaSM data object, LP1: Set the strategic direction)
- Test manager
- (→ YaSM role, Test manager)
- Test report
- A test report provides a detailed account of testing activities. A test report is created for example during tests of new or changed service components, or during tests of security or service continuity mechanisms.
(→ YaSM data object, LP3: Build new or changed services)
- Test script
- A test script specifies a set of test cases including their expected outcomes. The nature of the test cases will vary depending on what is to be tested.
(→ YaSM data object, LP3: Build new or changed services)
→ YaSM terms starting with "T"
→ Look up more YaSM terms
U
- Underpinning security policy
- Underpinning security policies are specific policies complementing the main security policy by setting binding rules, for example for the use of systems and information or the use and delivery of services.
(→ YaSM data object, SP7: Ensure security)
W
- Workforce and talent management
- (→ YaSM process, supporting processes > SP10: Manage human resources)
Y
- YaSM (Acronym)
- The acronym YaSM stands for "Yet another Service management Model". (See also: → What is YaSM?).
- YaSM service management processes
- (→ YaSM processes)
Notes
[1] YaSM® is a registered trade mark of IT Process Maps GbR.
[2] ITIL® and IT Infrastructure Library® are registered trademarks of the PeopleCert group.
[3] © Crown copyright 2011. Reproduced with permission from the Cabinet Office.
The YaSM glossary is based on: The YaSM Process Map - terms and definitions.
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() and Andrea Kempter
and Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
YaSM-Begriffe B › YaSM-Begriffe C › YaSM-Begriffe P › YaSM-Begriffe S