ITIL 4 vs ITIL V3: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<meta name="pinterest-rich-pin" content="false" /> | <meta name="pinterest-rich-pin" content="false" /> | ||
</itpmch> | </itpmch> | ||
<html | <html><div class="noresize"><a href="https://yasm.com/wiki/de/index.php/ITIL_4_vs_ITIL_V3"><img src="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/img/yasm-wiki/YaSM-Wiki-Deutsch.png" width="140" height="36" style="float:right;" alt="auf Deutsch" title="This page in German" /></a></div><br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
==ITIL 4: What's new?== | ==ITIL 4: What's new?== | ||
ITIL 4 - the most current edition of ITIL<sup><small>®</small></sup> [[#ITIL|[1]]] - was officially released in February 2019. As AXELOS state, "ITIL | ITIL 4 - the most current edition of ITIL<sup><small>®</small></sup> [[#ITIL|[1]]] - was officially released in February 2019. As AXELOS state, "ITIL 4 expands on previous versions by providing a practical and flexible basis to support organizations on their journey to the new world of digital transformation". | ||
ITIL V4 is thus an evolution of the familiar ITIL framework rather than a revolution, and still uses many [[#ITIL_4_components_vs._ITIL_V3|fundamental elements]] from the previous version ITIL V3, as first published in 2007 and updated in 2011 ("ITIL 2011"). In particular, many of the new [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes|ITIL V4 practices correspond to processes known from ITIL V3]]. | ITIL V4 is thus an evolution of the familiar ITIL framework rather than a revolution, and still uses many [[#ITIL_4_components_vs._ITIL_V3|fundamental elements]] from the previous version ITIL V3, as first published in 2007 and updated in 2011 ("ITIL 2011"). In particular, many of the new [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes|ITIL V4 practices correspond to processes known from ITIL V3]]. | ||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
| | | | ||
* The service value system (SVS) is a new concept in ITIL 4. The SVS describes "how all the components and activities in the organization work together to enable value creation". | * The service value system (SVS) is a new concept in ITIL 4. The SVS describes "how all the components and activities in the organization work together to enable value creation". | ||
* The | * The service value system includes five components: | ||
#[[#Guiding_principles|Guiding principles]], | #[[#Guiding_principles|Guiding principles]], | ||
#[[#Governance|Governance]], | #[[#Governance|Governance]], | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
#And [[#ITIL_4_practices|Practices]]. | #And [[#ITIL_4_practices|Practices]]. | ||
* ITIL V3, with its 26 service lifecycle processes, functions and other guidance arguably also describes how the components and activities in the organization work together. | * ITIL V3, with its 26 service lifecycle processes, functions and other guidance arguably also describes how the components and activities in the organization work together. | ||
* ITIL 4 and the SVS take a more holistic approach, providing organizations with a flexible operating model that supports different work approaches. ITIL 4 does not define specific | * ITIL 4 and the SVS take a more holistic approach, providing organizations with a flexible operating model that supports different work approaches. ITIL 4 does not define specific processes, and service providers are free to design tailor-made processes that work for their organizations. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|<h5>Guiding principles</h5> | |<h5>Guiding principles</h5> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
|<h5>Service value chain</h5> | |<h5>Service value chain</h5> | ||
| | | | ||
* The ITIL 4 service value chain is the central element in the | * The ITIL 4 service value chain is the central element in the service value system. It presents the key activities required to create value for customers. The six value chain activities are: | ||
#Plan, | #Plan, | ||
#Improve, | #Improve, | ||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
#Deliver and support. | #Deliver and support. | ||
*For each value chain activities, ITIL 4 outlines the key inputs and outputs. | *For each value chain activities, ITIL 4 outlines the key inputs and outputs. | ||
* The central element in ITIL V3 is the service lifecycle with five stages: Service strategy, design, transition, operation and continual service improvement. This lifecycle is not identical with the | * The central element in ITIL V3 is the service lifecycle with five stages: Service strategy, design, transition, operation and continual service improvement. This lifecycle is not identical with the service value chain, but on a more detailed level many of the activities in the ITIL V3 service lifecycle processes broadly correspond to the value chain activities. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|<h5>Continual improvement</h5> | |<h5>Continual improvement</h5> | ||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
* Instead of 26 processes, ITIL 4 presents 34 practices as "sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective". | * Instead of 26 processes, ITIL 4 presents 34 practices as "sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective". | ||
* It is in these practices where the roots of ITIL 4 in ITIL V3 are most visible, because many of the practices correspond to ITIL V3 processes. | * It is in these practices where the roots of ITIL 4 in ITIL V3 are most visible, because many of the practices correspond to ITIL V3 processes. | ||
* See below: [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes|A detailed comparison between ITIL | * See below: [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes|A detailed comparison between ITIL practices and ITIL processes]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
The idea behind organizing the ITIL processes in this way was to establish a Deming-like plan-do-check-act cycle focused on continual improvement. | The idea behind organizing the ITIL processes in this way was to establish a Deming-like plan-do-check-act cycle focused on continual improvement. | ||
ITIL V4 has dropped most references to the service lifecycle, but continual improvement has remained a key concept. For example, continual improvement is an element of the | ITIL V4 has dropped most references to the service lifecycle, but continual improvement has remained a key concept. For example, continual improvement is an element of the service value system, and the service value chain with its six activities (plan, improve, engage, design and transition, obtain/build, deliver and support) is very reminiscent of the ITIL V3 service lifecycle. | ||
== Where in ITIL 4 are the ITIL V3 processes? == | == Where in ITIL 4 are the ITIL V3 processes? == | ||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
<p>ITIL V3 defines 26 processes across the service lifecycle. In ITIL 4, these 26 processes have been replaced by 34 "practices" (<a href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/img/yasm-frameworks/itil/itil-4-practices-itil-v3-processes-comparison.jpg" title="ITIL 4 practices and ITIL V3 processes">see fig. 2</a>).</html> | <p>ITIL V3 defines 26 processes across the service lifecycle. In ITIL 4, these 26 processes have been replaced by 34 "practices" (<a href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/img/yasm-frameworks/itil/itil-4-practices-itil-v3-processes-comparison.jpg" title="ITIL 4 practices and ITIL V3 processes">see fig. 2</a>).</html> | ||
Some of them are new, but many of | Some of them are new, but many of these practices were formerly known as processes. | ||
For a detailed cross-reference, see chapter: [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes| | For a detailed cross-reference, see chapter: [[#ITIL_4_practices_vs._ITIL_V3_processes|Practices vs. processes]]. | ||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
<html>The tables below provide a detailed account of how the ITIL 4 practices map to the service lifecycle processes known from ITIL V3:</html> | <html>The tables below provide a detailed account of how the ITIL 4 practices map to the service lifecycle processes known from ITIL V3:</html> | ||
* [[# | * [[#ITIL_4_general_management_practices_and_related_ITIL_V3_processes|General management practices]] | ||
* [[# | * [[#ITIL_4_service_management_practices_and_related_ITIL_V3_processes|Service management practices]] | ||
* [[# | * [[#ITIL_4_technical_management_practices_and_related_ITIL_V3_processes|Technical management practices]] | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | {| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | ||
|+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%"> | |+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%">ITIL 4 general management practices and related ITIL V3 processes</h4> | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 manage­ment practice [[#ITIL-4-practices|[7]]] | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|Related ITIL V3 processes [[#ITIL-2011-processes|[8]]] | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|Related ITIL V3 processes [[#ITIL-2011-processes|[8]]] | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|Differences: ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4 | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|Differences: ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4 | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Archi­tecture manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL V3 includes an introduction to enterprise architecture management in the service strategy publication<sup>[[#ref-cabinet-office-2011a|[a]]]</sup>. | * ITIL V3 includes an introduction to enterprise architecture management in the service strategy publication<sup>[[#ref-cabinet-office-2011a|[a]]]</sup>. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Continual | |Continual improve­ment | ||
|The seven-step improve­ment process | |||
| | | | ||
* Continual improvement in ITIL 4 is about ongoing improvement of the organi­zation’s services, practices and all other elements required for the provision of services. | |||
* In ITIL V3, Continual service improve­ment (CSI) is the fifth stage of the service lifecycle. The ITIL V3 CSI publication<sup>[[#ref-cabinet-office-2011e|[e]]]</sup> describes CSI principles, methods and techniques and specifies one CSI process: The "seven-step improvement process". | |||
* Continual improvement in ITIL 4 is about ongoing improvement of the | * ITIL 4 advises that organi­zations use a continual improve­ment register (CRI) to manage their improvement ideas. This corresponds to the CSI register used in ITIL V3, and also to the service improvement plan (SIP). | ||
* In ITIL V3, Continual service | |||
* ITIL 4 advises that | |||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Infor­mation security manage­ment | ||
| | |Infor­mation security manage­ment, <br />access manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* One area of the security management practice in ITIL 4 is identity and access management, which corresponds to the ITIL V3 process of access management. | * One area of the security management practice in ITIL 4 is identity and access management, which corresponds to the ITIL V3 process of access management. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Knowledge | |Knowledge manage­ment | ||
| | |Knowledge manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Measure­ment and reporting | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL V3 does not define a measurement and reporting process, but | * ITIL V3 does not define a measurement and reporting process, but measure­ment and reporting are key activities in several ITIL processes, such as service level management and the seven-step improve­ment process. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Organi­zational change manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* Organizational change management (OCM) is a set of | * Organizational change management (OCM) is a set of manage­ment techniques and capabilities rather than a process. | ||
* OCM addresses the human side of changes and is different from the ITIL V3 process of change | * OCM addresses the human side of changes and is different from the ITIL V3 process of change manage­ment (which aims to minimize risk from changes to the operating environment). | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Portfolio | |Portfolio manage­ment | ||
| | |Service portfolio manage­ment, <br />business relation­ship manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* The ITIL 4 practice of portfolio management refers to various types of portfolios, such as service, project and customer portfolios. | * The ITIL 4 practice of portfolio management refers to various types of portfolios, such as service, project and customer portfolios. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Project | |Project manage­ment | ||
| | |Transition planning and support | ||
| | | | ||
* The ITIL V3 process of transition planning and support, part of the service transition lifecycle stage, is primarily about planning and | * The ITIL V3 process of transition planning and support, part of the service transition lifecycle stage, is primarily about planning and coor­dinating service transition projects. | ||
* The ITIL 4 practice of project management is broader in scope. It aims to ensure that all projects in the | * The ITIL 4 practice of project management is broader in scope. It aims to ensure that all projects in the organi­zation are completed successfully. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Relation­ship manage­ment | ||
| | |Business relation­ship manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* Relationship management in ITIL 4 refers to | * Relationship management in ITIL 4 refers to relation­ships with all stake­holders of the organization, including customers. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Risk | |Risk manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* Risk | * Risk manage­ment is not on the list of ITIL V3 processes, but risk management techniques are described in several ITIL processes, and ITIL V3 calls for "coordinated risk assessment exercises". | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service financial | |Service financial manage­ment | ||
| | |Financial manage­ment for IT services | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Strategy | |Strategy manage­ment | ||
| | |Strategy manage­ment for IT services | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Supplier | |Supplier manage­ment | ||
| | |Supplier manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* The ITIL 4 practice of supplier management includes new guidance on multi-sourcing and service integration (an established concept from the SIAM™ framework). | * The ITIL 4 practice of supplier management includes new guidance on multi-sourcing and service integration (an established concept from the SIAM™ framework). | ||
* ITIL 4 has dropped the ITIL V3 term underpinning contract (UC) and uses more generic terms instead (contract, agreement, warranty | * ITIL 4 has dropped the ITIL V3 term underpinning contract (UC) and uses more generic terms instead (contract, agreement, warranty require­ments, etc.). | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Workforce and talent | |Workforce and talent manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL V3 does not include a specific process for workforce and talent management. | * ITIL V3 does not include a specific process for workforce and talent management. | ||
| Line 317: | Line 306: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | {| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | ||
|+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%"> | |+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%">ITIL 4 service management practices and related ITIL V3 processes</h4> | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 manage­ment practice | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|Related ITIL V3 processes | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|Related ITIL V3 processes | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL V4 vs. V3: The changes | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL V4 vs. V3: The changes | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Availa­bility manage­ment | ||
| | |Availa­bility manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
| Line 331: | Line 319: | ||
|Business analysis | |Business analysis | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* This ITIL 4 practice describes techniques for analyzing systems, processes, architectures, etc. | * This ITIL 4 practice describes techniques for analyzing systems, processes, architectures, etc. | ||
* Some of these techniques are applied in ITIL V3 processes, for instance as service | * Some of these techniques are applied in ITIL V3 processes, for instance as service require­ments are defined during the service design stage. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Capacity and | |Capacity and per­formance manage­ment | ||
| | |Capacity manage­ment, <br />demand manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Change | |Change enable­ment | ||
| | |Change manage­ment, <br />change evaluation | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Incident | |Incident manage­ment | ||
| | |Incident manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|IT asset | |IT asset manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL 4 introduces IT asset management (ITAM) as the practice that <i>"aims to manage the lifecycles and total costs of all IT assets ( | * ITIL 4 introduces IT asset management (ITAM) as the practice that <i>"aims to manage the lifecycles and total costs of all IT assets (finan­cially valuable components)"</i>. ITAM is sometimes referred to as 'financial asset manage­ment' or 'fixed asset management'. | ||
* ITIL V3 includes an overview of IT asset management activities and concepts as part of the service asset and | * ITIL V3 includes an overview of IT asset management activities and concepts as part of the service asset and configu­ration manage­ment process, but otherwise states that fixed asset management is not described in detail. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Monitoring and event | |Monitoring and event manage­ment | ||
| | |Event manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Problem | |Problem manage­ment | ||
| | |Problem manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Release | |Release manage­ment | ||
|Release and deploy­ment manage­ment | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL 4 includes some additional guidance for managing releases in Agile / DevOps environments. | |||
* ITIL 4 includes some additional guidance for managing releases in Agile/DevOps environments. | |||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service catalogue | |Service catalogue manage­ment | ||
| | |Service catalogue manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service | |Service configu­ration manage­ment | ||
| | |Service asset and configu­ration manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service | |Service conti­nuity manage­ment | ||
| | |IT service conti­nuity manage­ment (ITSCM) | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service design | |Service design | ||
|Design coor­dination, <br />service level manage­ment | |||
| | | | ||
* Service design is the second service lifecycle stage in ITIL V3, with design coordination and service level manage­ment as key processes. | |||
* Service design is the second service lifecycle stage in ITIL V3, with design coordination and service level | |||
* Service design in ITIL V3 includes further processes such as capacity management, availability management, IT service continuity management, etc., which correspond to the ITIL 4 practices of the same names. | * Service design in ITIL V3 includes further processes such as capacity management, availability management, IT service continuity management, etc., which correspond to the ITIL 4 practices of the same names. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service desk | |Service desk | ||
| | |Incident manage­ment, <br />request fulfill­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* ITIL V3 refers to the service desk as a "function", whose activities are described in the incident management and request fulfilment processes. | * ITIL V3 refers to the service desk as a "function", whose activities are described in the incident management and request fulfilment processes. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service level | |Service level manage­ment | ||
| | |Service level manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service request | |Service request manage­ment | ||
| | |Request fulfill­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Service | |Service valida­tion and testing | ||
| | |Service valida­tion and testing | ||
| | | | ||
* -- | * -- | ||
| Line 435: | Line 405: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | {| class="wikitable" style="background: white;" | ||
|+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%"> | |+style="background:#465674;"|<h4 style="color:#ffffff; font-size: 120%">ITIL 4 technical management practices and related ITIL V3 processes</h4> | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 4 manage­ment practice | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|Related ITIL V3 processes | !style="background:#eeeeee; "|Related ITIL V3 processes | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4: The changes | !style="background:#eeeeee;"|ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4: The changes | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Deploy­ment manage­ment | ||
| | |Release and deploy­ment manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
* The ITIL 4 practice of deployment management explains various approaches to the deployment of hardware, software and other service components into the live environment. | * The ITIL 4 practice of deployment management explains various approaches to the deployment of hardware, software and other service components into the live environment. | ||
| Line 449: | Line 418: | ||
* ITIL 4 provides some additional advice for environments with multiple suppliers. | * ITIL 4 provides some additional advice for environments with multiple suppliers. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
| | |Infra­structure and platform manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* This ITIL 4 practice is concerned with governing the use of technologies in the organization, including updated guidance on cloud services and cloud computing. | * This ITIL 4 practice is concerned with governing the use of technologies in the organization, including updated guidance on cloud services and cloud computing. | ||
* There is very limited guidance on this topic in ITIL V3. The service strategy publication<sup>[[#ref-cabinet-office-2011a|[a]]]</sup> includes an appendix with an introduction to cloud offerings and their impact on the service strategy. | * There is very limited guidance on this topic in ITIL V3. The service strategy publication<sup>[[#ref-cabinet-office-2011a|[a]]]</sup> includes an appendix with an introduction to cloud offerings and their impact on the service strategy. | ||
|-style="vertical-align:top" | |-style="vertical-align:top" | ||
|Software | |Software develop­ment and manage­ment | ||
| | | | ||
-- | |||
| | | | ||
* ITIL 4 provides a high-level overview of software development and management activities. | * ITIL 4 provides a high-level overview of software development and management activities. | ||
| Line 511: | Line 480: | ||
<meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="Differences: ITIL V3 vs V4" /> | <meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="Differences: ITIL V3 vs V4" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4" /> | <meta itemprop="alternativeHeadline" content="ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4" /> | ||
<link itemprop="url" href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/index.php/ITIL_4_vs_ITIL_V3" /> | <link itemprop="url" href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/index.php/ITIL_4_vs_ITIL_V3" /> <meta itemprop="dateCreated" content="2014-06-05" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="dateCreated" content="2019-03-16" /> | |||
<meta itemprop="datePublished" content="2019-03-16" /> | |||
<meta itemprop="dateModified" content="2021-09-29" /> | |||
<link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/img/yasm-frameworks/itil/itil-4-vs-itil-v3-list.jpg" /> | <link itemprop="primaryImageOfPage" href="https://yasm.com/wiki/en/img/yasm-frameworks/itil/itil-4-vs-itil-v3-list.jpg" /> | ||
<meta itemprop="inLanguage" content="en" /> | <meta itemprop="inLanguage" content="en" /> | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 29 September 2021
Differences between ITIL V3 2011 and the new version of ITIL 4.
Organizations that need to plan their transition to the latest edition of ITIL® [1] will require a detailed mapping between ITIL V3 and ITIL 4: This page describes in detail where ITIL V4 has added new guidance, and how the contents in ITIL 4 can be traced back to specific elements of ITIL V3.
ITIL 4: What's new?
ITIL 4 - the most current edition of ITIL® [1] - was officially released in February 2019. As AXELOS state, "ITIL 4 expands on previous versions by providing a practical and flexible basis to support organizations on their journey to the new world of digital transformation".
ITIL V4 is thus an evolution of the familiar ITIL framework rather than a revolution, and still uses many fundamental elements from the previous version ITIL V3, as first published in 2007 and updated in 2011 ("ITIL 2011"). In particular, many of the new ITIL V4 practices correspond to processes known from ITIL V3.
Differences between ITIL V3 and V4
| ITIL V4 component [2] | Differences: New content in ITIL V4 and how it relates to ITIL V3 [3] |
|---|---|
ITIL 4 key concepts | |
| Key concepts of service management |
|
ITIL 4 four dimensions model | |
| The four dimensions of service management |
|
ITIL 4 service value system (SVS) | |
| Service value system overview |
|
Guiding principles |
|
Governance |
|
Service value chain |
|
Continual improvement |
|
ITIL 4 practices |
|
Has ITIL V4 dropped the ITIL V3 service lifecycle?
A key innovation of ITIL V3 was the introduction of the service lifecycle, consisting of five service lifecycle stages (service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation and continual service improvement). The ITIL V3 processes are distributed across this service lifecycle; for instance, the incident management process is part of the service operation stage.
The idea behind organizing the ITIL processes in this way was to establish a Deming-like plan-do-check-act cycle focused on continual improvement.
ITIL V4 has dropped most references to the service lifecycle, but continual improvement has remained a key concept. For example, continual improvement is an element of the service value system, and the service value chain with its six activities (plan, improve, engage, design and transition, obtain/build, deliver and support) is very reminiscent of the ITIL V3 service lifecycle.
Where in ITIL 4 are the ITIL V3 processes?
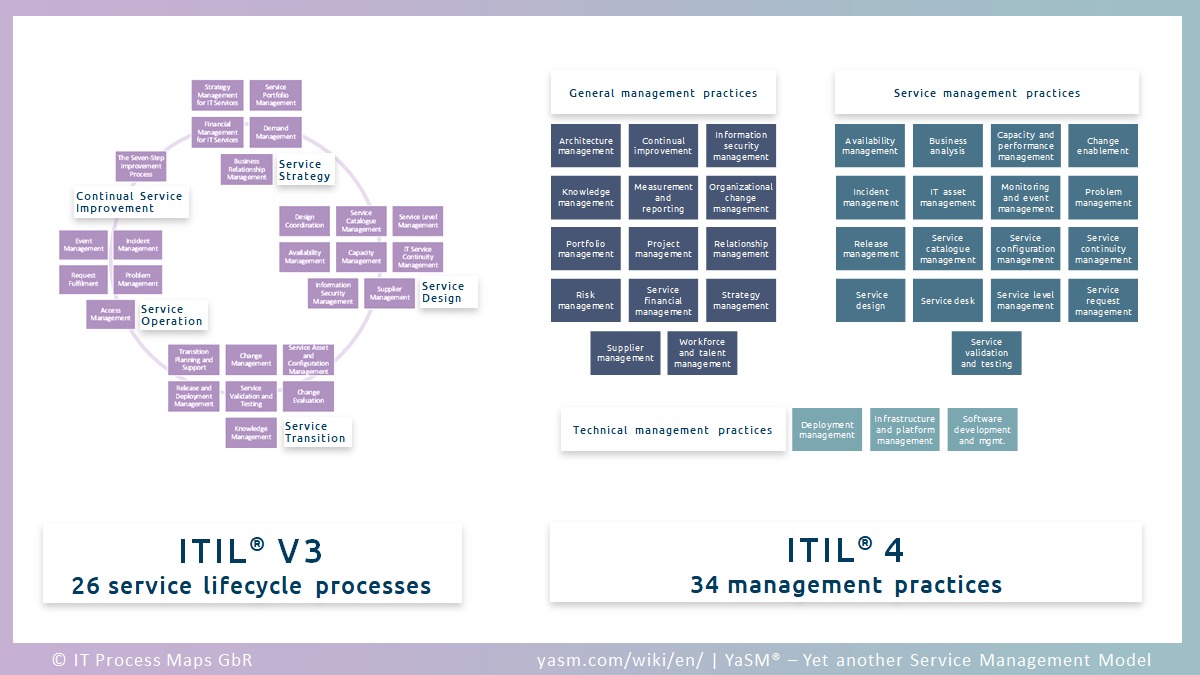
34 management practices (ITIL 4) vs. 26 service lifecycle processes (ITIL V3).
ITIL V3 defines 26 processes across the service lifecycle. In ITIL 4, these 26 processes have been replaced by 34 "practices" (see fig. 2).
Some of them are new, but many of these practices were formerly known as processes.
For a detailed cross-reference, see chapter: Practices vs. processes.
So the ITIL V3 processes are still alive, and what is more, the authors of ITIL 4 state that ITIL V3 is still valid guidance that can be used for defining service management processes.
But it is also worth noting that ITIL 4 is not prescriptive about processes, and gives service providers more freedom to design tailor-made processes that work for the organization.
This presents an opportunity for a fresh start with ITIL 4 processes, in line with the advice in ITIL 4 to "keep things simple and practical":
The YaSM® process model describes a streamlined, clear-cut set of service management processes that is a good match for the leaner, more flexible operating models favored by today's service provider organizations.
ITIL 4 practices vs. ITIL V3 processes
The tables below provide a detailed account of how the ITIL 4 practices map to the service lifecycle processes known from ITIL V3:
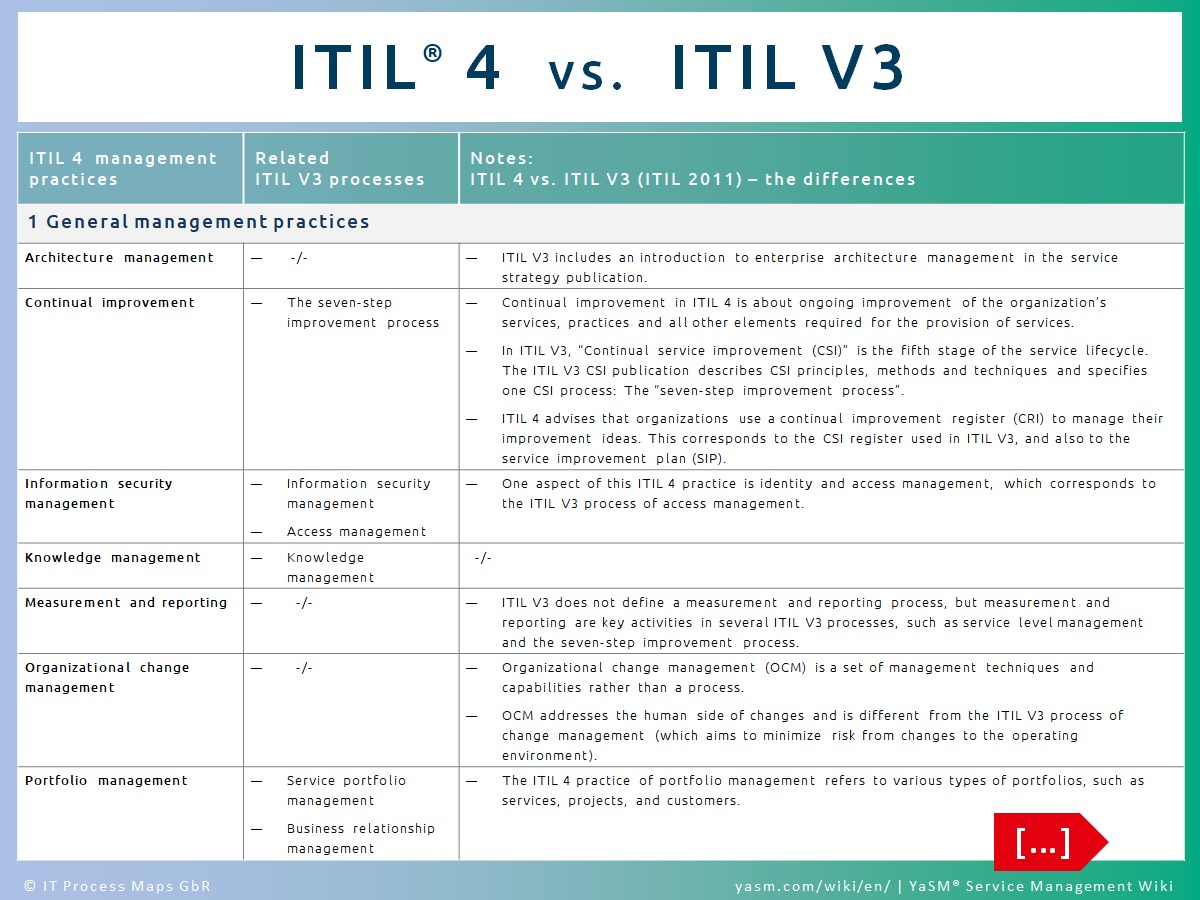
| ITIL 4 management practice [7] | Related ITIL V3 processes [8] | Differences: ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture management |
-- |
|
| Continual improvement | The seven-step improvement process |
|
| Information security management | Information security management, access management |
|
| Knowledge management | Knowledge management |
|
| Measurement and reporting |
-- |
|
| Organizational change management |
-- |
|
| Portfolio management | Service portfolio management, business relationship management |
|
| Project management | Transition planning and support |
|
| Relationship management | Business relationship management |
|
| Risk management |
-- |
|
| Service financial management | Financial management for IT services |
|
| Strategy management | Strategy management for IT services |
|
| Supplier management | Supplier management |
|
| Workforce and talent management |
-- |
|
| ITIL 4 management practice | Related ITIL V3 processes | ITIL V4 vs. V3: The changes |
|---|---|---|
| Availability management | Availability management |
|
| Business analysis |
-- |
|
| Capacity and performance management | Capacity management, demand management |
|
| Change enablement | Change management, change evaluation |
|
| Incident management | Incident management |
|
| IT asset management |
-- |
|
| Monitoring and event management | Event management |
|
| Problem management | Problem management |
|
| Release management | Release and deployment management |
|
| Service catalogue management | Service catalogue management |
|
| Service configuration management | Service asset and configuration management |
|
| Service continuity management | IT service continuity management (ITSCM) |
|
| Service design | Design coordination, service level management |
|
| Service desk | Incident management, request fulfillment |
|
| Service level management | Service level management |
|
| Service request management | Request fulfillment |
|
| Service validation and testing | Service validation and testing |
|
| ITIL 4 management practice | Related ITIL V3 processes | ITIL 3 vs. ITIL 4: The changes |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment management | Release and deployment management |
|
| Infrastructure and platform management |
-- |
|
| Software development and management |
-- |
|
References
[AXELOS, 2019]. -- AXELOS: ITIL® Foundation, ITIL 4 Edition. - The Stationery Office; Norwich, UK, February 2019.
[a] [Cabinet Office, 2011a]. -- The Cabinet Office: ITIL® Service Strategy (2011 Edition). - The Stationery Office; London, UK, July 2011.
[b] [Cabinet Office, 2011b]. -- The Cabinet Office: ITIL® Service Design (2011 Edition). - The Stationery Office; London, UK, July 2011.
[c] [Cabinet Office, 2011c]. -- The Cabinet Office: ITIL® Service Transition (2011 Edition). - The Stationery Office; London, UK, July 2011.
[d] [Cabinet Office, 2011d]. -- The Cabinet Office: ITIL® Service Operation (2011 Edition). - The Stationery Office; London, UK, July 2011.
[e] [Cabinet Office, 2011e]. -- The Cabinet Office: ITIL® Continual Service Improvement (2011 Edition). - The Stationery Office; London, UK, July 2011.
Notes
[1] ITIL® is a registered trade mark of AXELOS Limited.
[2] The ITIL 4 content referenced in this table is based on ITIL 4 Foundation, published in February 2019.
[3] The ITIL V3 content referenced in this table is based on the 2011 edition of ITIL V3.
[4] YaSM® is a registered trademark of IT Process Maps GbR.
[5] SIAM™ is a registered trademark of EXIN.
[6] VeriSM™ is a registered trademark of IFDC.
[7] The management practices in this table are based on ITIL 4 Foundation, published in February 2019.
[8] The ITIL processes in this table are based on ITIL V3 2011.
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() and Andrea Kempter
and Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
What's new? › Differences: ITIL V3 and V4 › Service lifecycle in ITIL 4 › ITIL 4 processes › ITIL 4 practices vs. ITIL V3 processes




