Service Management
Service management is a management discipline aimed at providing quality services that customers will value, buy and use.
As a professional domain, service management has been maturing for decades. Today, organizations that provide services can tap into a huge body of knowledge, including various frameworks and standards that describe service management principles, best practices and processes.
Why service management is ever more important
Services help organizations to build long-term relationships with their customers.
Most companies seek to develop innovative and unique products to maintain a competitive edge. However, services enable businesses to enter into a dialogue with their customers. Businesses are thus able to keep a pulse on their clients' changing preferences and concerns, and adapt their range of products and services accordingly.
The goal of top-quality service is a happy, loyal customer base.
Watch the video: How service management helps organizations build up a loyal customer base, and why the topic is getting a lot of attention these days.
- "What is service management?" (10:33 min.)
What is "good" service management?
Service management should always start with the service consumer: Service providers need to understand their consumers to develop and offer an attractive range (or "portfolio") of services.
To this end, service providers will typically
- identify customer journeys,
- describe how their services create value, and
- define the service properties in line with customer requirements.
Other key elements of service management are
- continual improvement and
- the service lifecycle.
These concepts enable organizations to adapt quickly to shifts in the marketplace. Consumer needs change over time, new technologies become available and new ideas emerge, so the portfolio of services provided to customers is highly dynamic.
Therefore, service providers use feedback from customers, market surveys and other input to continually adapt and improve their services, thus ensuring customer loyalty and business growth.
- The customer is king. - Part 1 of our video series about the "simple principles of good service management".
- Vaguely defined services can't be managed. - The simple principles of good service management, part 2.
What are the key service management processes or practices?
All service management frameworks describe the essential activities of good service management as processes or practices. ITIL®, for example, provides guidance for 34 service management practices.
A key principle underpinning the frameworks is the service lifecycle concept. This lifecycle is a variant of the "Plan-Do-Check-Act" or "PDCA" cycle, a well-established management method for continual improvement.
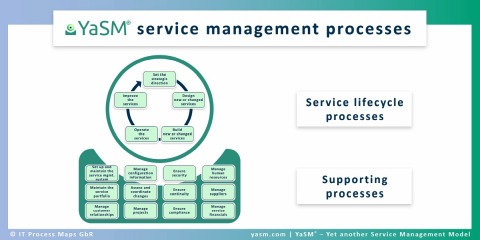
Service lifecycle and supporting processes in the YaSM model (➜ details)
The service lifecycle consists of five stages which broadly correspond to the following service management processes or practices:
- Service strategy
- Service design
- Service transition
- Service operation, including incident management, service request management and problem management
- Service improvement.
Other service management practices include
- Service portfolio management, including service catalogue management
- Customer relationship management
- Configuration management
- Change management
- Service continuity management
- etc.
These are examples of processes, practices, capabilities or knowledge areas described in the various service management frameworks.
In the YaSM service management model, we have identified a streamlined set of 19 key processes (see fig. 2: "YaSM processes") that organizations can choose from as they start to adopt service management best practice.
What service management frameworks are available?
The service management body of knowledge is mostly made up of various frameworks that describe best practices and standard processes.
Using one of these frameworks helps organizations to follow a disciplined approach to service management implementation.
The first widely adopted service management framework has been ITIL® (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). ITIL was first introduced in the 1980s through the United Kingdom’s Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA), after UK government officials felt the level of IT services they were receiving were both costly and inefficient.
Over the years, ITIL has been updated several times and today is the most popular service management framework.
However, ITIL is not the only service management guideline around. There are alternative frameworks and approaches that organizations can consider, such as
- COBIT® (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology)
- CMMI-SVC® (CMMI for Services)
- FitSM (Federated IT Service Management)
- SIAM™ (Service Integration and Management)
- VeriSM™.
Organizations can meet their different requirements by integrating several frameworks, processes and standards into their approach to managing services.
IT service management (ITSM) and enterprise service management (ESM)
Most of these frameworks started their life with a focus on IT service management (ITSM), and they still include lots of guidance for the use of technology.
But it has always been true that a service is a service, no matter whether it is an IT or a non-IT service, and as such the ideas behind ITSM can also be applied to other areas of a business, including HR, sales, marketing, facilities, etc. This growing trend of applying ITSM principles outside of IT has become to be known as "enterprise service management (ESM)".
Today, most frameworks have dropped the distinction between ITSM and ESM and simply relate to "service management".
What are the differences between the various service management frameworks?
Although the most widely used service management frameworks share the same roots and are very much in line with the principles first formulated in ITIL, each framework addresses specific industries or business needs:
- ITIL describes a service value system and best practices for delivering IT and business services.
- COBIT is a governance framework that defines a set of controls for the management of IT.
- CMMI-SVC provides guidance for developing or improving processes that meet the business goals of the organization.
- FitSM provides a standard for the effective management of IT services (ITSM).
- SIAM aims at integrating interdependent services from various internal and external service providers into end-to-end services.
- VeriSM shows organizations how they can adopt a range of management practices in a flexible way to deliver the right product or service.
ISO 20000, the international standard for service management
ISO/IEC 20000 is the international standard for service management, published by ISO (the International Organization for Standardization).
The standard is based on the fundamental principles of ITIL. It does, however, not describe service management processes or practices in detail, but defines requirements for a service management system.
ISO 20000 certification for organizations is essentially the evidence that service management best practices have been implemented.
ISO 20000 offers businesses a competitive edge by allowing them a chance to receive an organizational certificate. To do this, organizations must pass an audit conducted by a Registered Certification Body.
How does YaSM compare with the service management frameworks?
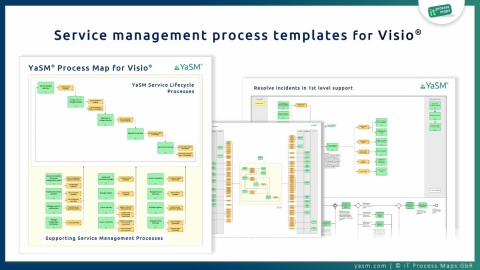
The YaSM process model for Visio® (➜ details)
The YaSM process model is not another framework. It is rather a translation of the vast amount of guidance provided in the service management frameworks into a streamlined, accessible set of processes and document templates (see fig. 3).
YaSM has a clear, consistent structure that helps organizations understand the ideas behind service management.
Also, the YaSM model is not merely read-only information:
All diagrams and documents are fully editable templates, so businesses do not have to start from nothing as they design the service management processes for their organization. YaSM is thus used by organizations to accelerate their adoption of service management best practice.
For more detailed information and examples of the diagrams and documents included in the YaSM process model, please refer to the platform-specific pages about the YaSM Process Map for Visio and the YaSM Process Map for ARIS.
See also: YaSM and ITIL® (ITIL 4), COBIT®, CMMI-SVC®, FitSM, SIAM™, and VeriSM™.
What are the benefits of service management?
There are many areas where an organization can benefit from adopting service management best practice, including
- better alignment of services with business, customer and user demands
- improved ability to learn from previous experience
- best use of resources
- communicated roles and responsibilities in service provision
- elimination of redundant work.
Related topics
- What is a service, and what are common types of services?
- Service management implementation - a roadmap for organizations that seek to improve their service management
- YaSM service management processes
- More information about the popular service management frameworks: ITIL® and ITIL 4, COBIT®, CMMI-SVC®, FitSM, SIAM™ and VeriSM™
Notes
By: Stefan Kempter ![]() and Andrea Kempter
and Andrea Kempter ![]() , IT Process Maps.
, IT Process Maps.
What is service management? › Goals / relevance › 'Good' service management › Key processes or practices › Frameworks › Service mgmt. process model